Intro to XHTML series
11. How to give your web page some structure
Now, it's time to finally give our web page some content. But remember, you can't put text directly inside the body -- only tags.
(X)HTML has several structural tags that are specifically designed to contain text and to divide up the page into logical parts.
The first of these is the <div> tag. divs can contain text and inline elements, as well as other divs, and pretty much any other content tag.
(X)HTML has two main types of content elements -- inline elements and block elements.
Inline elements -- text formatting tags, img tags, form input tags, etc. -- are those that either apply to text or should be treated as text, flowing about the document's structure wherever they can.
That structure is defined by block elements, which have a clearly-defined rectangular shape. div is a block element.
Like text, inline elements cannot be contained directly by body. Instead, they must go inside a block element.
1) Let's add a div now.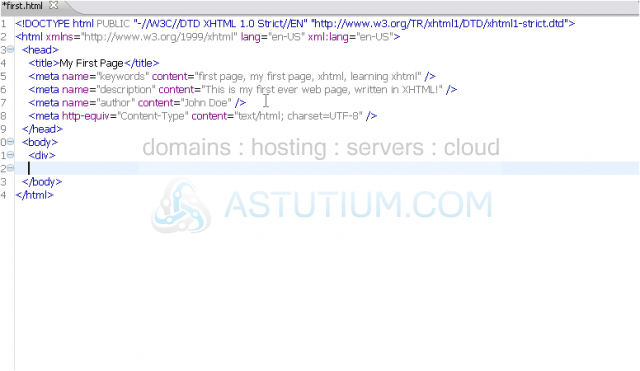
<div> is a pretty broad tag, with no specific purpose other than to group together areas of content. When possible, you should still not put text or inline elements directly inside a div, but instead enclose them inside a more specific element.
One of these is the paragraph tag, <p>, which is also a block element. You'll learn about some of the others later.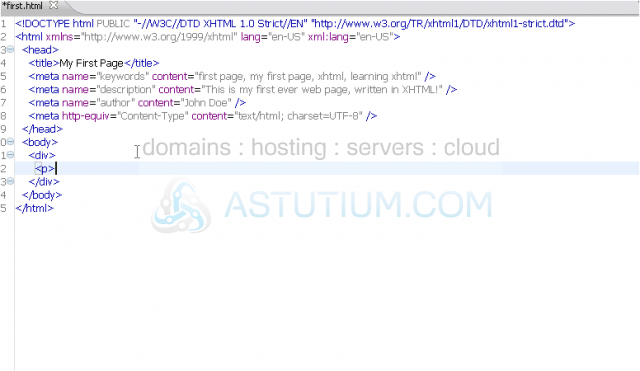
2) Now, we'll put a paragraph tag in our div.
3) Finally, for some text.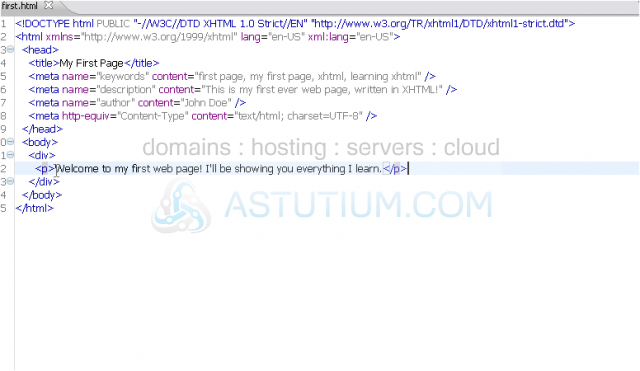
4) We can put as many elements inside a div as we want, so let's add another paragraph.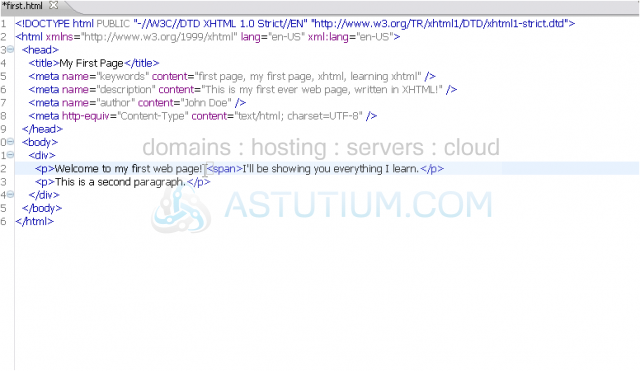
The final element we'll show you today is the <span> element. Without some more advanced knowledge of XHTML and CSS, you won't understand its full potential, but you should still know about it.
This tag is used to define a span of text or other inline elements. span itself is an inline element.
5) Let's wrap a <span> tag around this second sentence.
All three tags you've learned about in this tutorial will be very useful when applying CSS styles to a web page.
6) Now, let's Save the web page and take a look at it in our browser.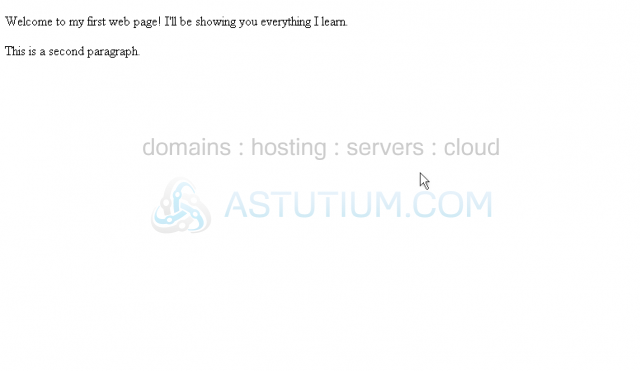
By default, the <div> and <span> tags will not affect the elements they contain.
The <p> tag, however, usually has a top and bottom margin, which we can see by the spaces above and in between our two paragraphs.
This is the end of the tutorial. You now know a little bit about three structural tags, and what inline and block elements are.